For the skin and body, collagen is super important. It’s not just a beauty trend that has spread from cosmetic injections to products that you see every day on drugstores and grocery shelves. Food, food supplements, skin creams, powders, and even drinks use collagen as a way to a healthy and vibrant body. But what does it actually do?
What is Collagen?
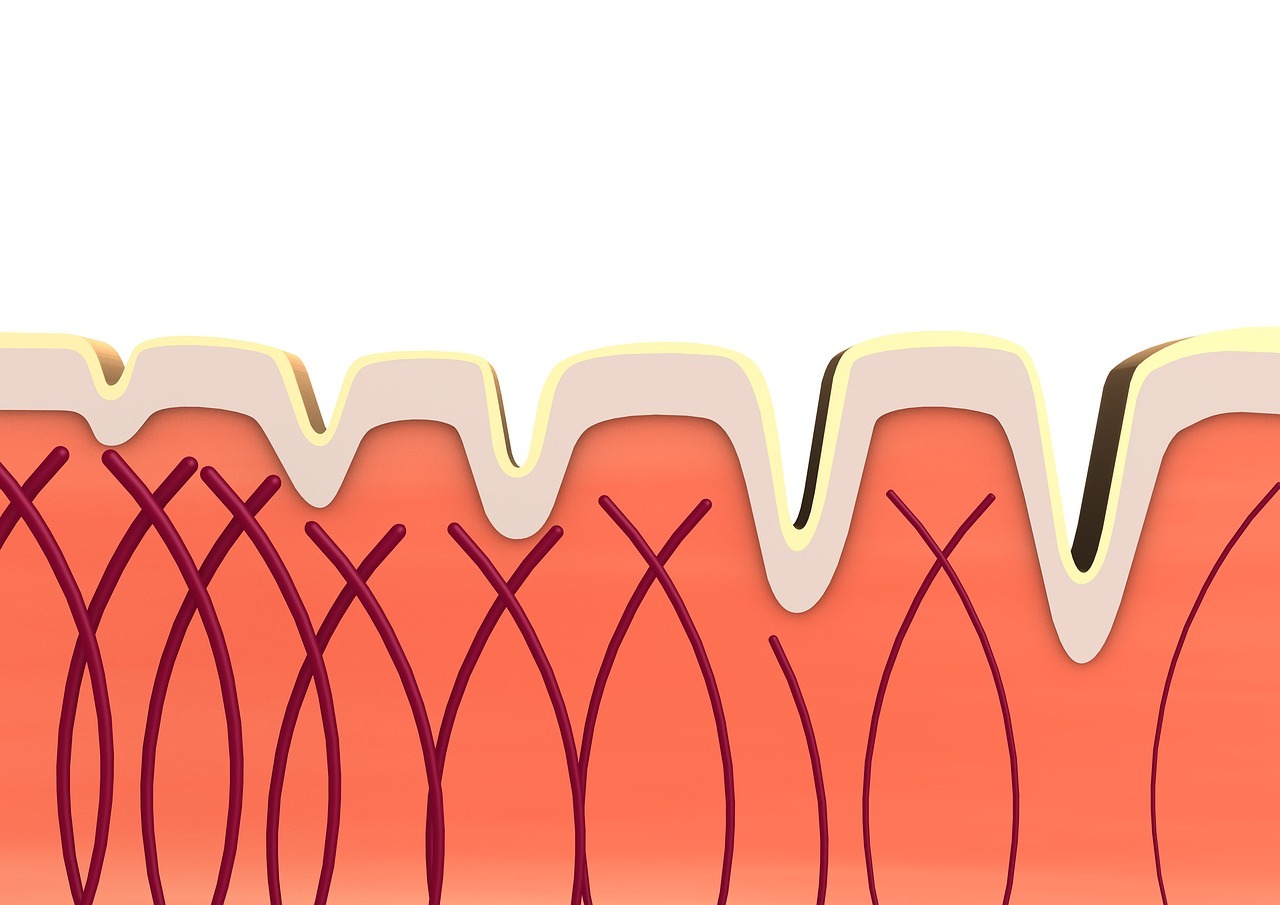
Collagen is a protein behind healthy skin and joints and is the most abundant protein in the body. It’s basically the protein or “glue” that holds the entire body together. It accounts for around a third of the body’s protein composition, as it forms the connective tissue for almost all structures in the body. It has an essential role in providing structure to the skin and helping the blood clot. It’s considered as one of the building blocks to bones, muscles, skin, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, as well as other body parts such as teeth, blood vessels, and corneas.
In the human body, there are at least 16 types of collagen, with four main types:
- Type 1 – This type of collagen comprises 90% of the collagen in the body, and it’s made of densely packed fibers. It improves skin structure, tendons, bones, connective tissue, fibrous cartilage, and teeth.
- Type 2 – This type of collagen is found in elastic cartilages that cushion joints, and it’s made of more loosely packed fibers.
- Type 3 – This type supports muscle structures, as well as structures of arteries and organs.
- Type 4 – This type is found in layers of skin, which helps with filtration.
What happens if your body does not have enough collagen?
The level of collagen isn’t something to be measured, but you can easily tell when it’s falling. The collagen decreases as you get older, which contributes to wrinkles, fine lines, and visible signs of aging on the skin.
Decreased collagen levels can also cause stiffer and less flexible tendons and ligaments, joint pain and osteoarthritis, weakening muscles, and gastrointestinal problems caused by thinning of the digestive tract lining.
How do you prevent collagen drop?
The body produces less and lower-quality collagen when you age. It’s inevitable. Besides aging, the reason why people don’t have enough collagen is they have a poor diet. The body can’t produce enough collagen if it doesn’t receive the necessary elements and nutrients.
While you can’t prevent aging, you can prevent your body from producing less collagen by avoiding collagen-destroying behaviors such as smoking, exposure to too much sunshine, and consuming added sugar and refined carbs. Smoking and ultraviolet radiation can reduce the production of collagen, while sugar interferes with collagen’s ability to repair itself.
Also, autoimmune diseases like lupus can cause a decrease in collagen production in the body.
What can you do to boost collagen production?
When your body produces collagen, it combines amino acids called glycine and proline. The process also requires zinc, vitamin C, and copper. You may help your body produce collagen by making sure you get a regular dose of these healthy foods for their collagen-boosting components:
High-quality protein sources such as meat, poultry, seafood, tofu, dairy, and legumes are all sources of amino acids. Bone broth is also a collagen-boosting brew.
- Proline can be found in egg whites, cabbage, dairy products, mushrooms, asparagus, and wheat germ.
- Citrus fruits like orange and lemons, strawberries, and bell peppers are high producers of vitamin C.
- Glycine can be found mostly in gelatin, pork skin, and chicken skin, but it’s also a component in various protein-containing foods.
- Copper is found in large amounts in sesame seeds, organ meats, cocoa powder, cashews, and lentils.
If you have a healthy diet and you’re feeding your body enough nutrients, it needs to produce collagen; you don’t need a supplement. But there’s nothing wrong with taking one. So besides food, you can also rely on supplements to boost your collagen levels. Taking collagen-rich supplements can slow down the effects of aging on your skin, keeping you youthful-looking for longer.
What are the benefits of collagen supplements?
Collagen supplements usually come in the form of hydrolyzed collagen (or collagen peptide) powder. It usually has no flavor and can be added to anything – your beverages, soups, smoothies, and sauces. It brings an added protein boost and helps reduce wrinkles, support healthy joints, and increase skin hydration.
With supplements, collagen is hydrolyzed in a process that breaks down proteins in a smooth and light powder. It means that your body has an easier time digesting, distributing, and absorbing the amino acids throughout the body. In short, this process makes the amino acids available to be used by your body upon intake.
There are several benefits of taking collagen supplements, such as:
- Improves skin health, strengthening the skin and boosting hydration and elasticity
- Helps protect joints, maintain the integrity of your cartilage, and relieve joint pain
- Keeps bones strong, preventing bone loss and deterioration
- Boosts muscle mass, keeping your muscles strong and functioning properly
- Promotes heart health, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases
- Strengthens nails and prevents brittleness
Can collagen creams do wonders for the skin?
In the beauty world, collagen is prized for its anti-aging abilities. Since it’s a major component of the skin, it plays a big role in strengthening the skin. Plus, every desirable characteristic of a healthy skin comes down to collagen content. The more protein we have, the plumper, the firmer, and juicier our skin looks like. But as mentioned earlier, collagen starts to break down as we get older. It causes loss of plumpness, fullness, and brings wrinkles.
As for skin creams with synthetic collagen, you won’t know for sure if it can work. But using a skin cream is not as effective as eating healthy and protecting your skin from sunburns and excessive sun exposure.
So does that mean that using collagen creams is useless? Consider this picture:
The structure of collagen protein is like a rope or a braid. Individual amino acids link up to form long chains that bundle together to form thicker strands. These strands then twist up and coil around each other to build multiple triple helices. And these helices connect from one end to another and stack on top of each other to form clusters called fibrils. This means that collagen is a massive and complex molecule.
This is why creams that claim to be formulated with pure collagen can’t easily live up to its claims – the massive collagen molecules are simply too big to penetrate the epidermis and definitely too big to go down to the dermis where it can really cause an effect on the skin. Even though collagen creams feel gentle and moisturizing to the skin, that’s mostly its benefit.
To get around this issue, most creams, lotions, potions, and pills that tout collagen as the main ingredient actually contains hydrolyzed collagen or collagen peptides. This collagen has been broken down into smaller chains and can penetrate the outer skin barrier and make its way into the dermis. But while it seems like a plausible idea and can help increase collagen production in the long run, this theory hasn’t been tested, let alone proven experimentally.
Meanwhile, studies have suggested that oral collagen can improve skin appearance. According to recent studies, taking collagen peptides in an oral form brings improved skin elasticity, hydration, and wrinkling. But either way, it’s mild, and if you’re already eating a normal, balanced diet, you are getting all the collagen you need.
While collagen creams won’t make a huge difference for your skin, it’s also harmless and can work as an effective and efficient moisturizer. If your focus is increasing collagen and minimizes collagen loss, sunscreen may even be more effective, as it prevents your existing collagen from breaking down. Another better option is retinoid because it has more evidence for building collagen.