The Paris-based LVMH Group is a French multinational corporation. The company mainly focuses on high-end apparel, jewelry, accessories, cosmetics, and timepieces. It is the largest luxury goods company in the world, earning $8.4 billion in profit on revenues of $62.5 billion in 2019.
Alan Chevalier and Henry Recamier established the firm in 1987 after Louis Vuitton and Moët Hennessy merged. It owns around 60 firms, many of which are luxury cosmetics and some of which have their daughter companies. That brings the company’s total number of brands to 75. LVMH is a parent company of Dior.
The Birth of a Luxury Giant: The Founding of Louis-Vuitton-Moët-Hennessy
Alain Chevalier and Henry Recamier established the LVMH company in 1987. The corporation is just a few decades old, yet its roots go back nearly three centuries. Moët&Chandon, Hennessy, and Louis Vuitton, the forerunners to LVMH, all got their starts in business in 1743, 1765, and 1854, respectively. If you are also interested to learn about the history of Louis Vuitton, you may read our post, How Did Louis Vuitton Become the Symbol of Luxury Fashion?
The French winemaker Moët & Chandon enjoyed great success during its heyday. In the 1820s, yearly sales averaged around 20,000 bottles. LVMH has a long history of growth and expansion, including exporting goods to the United States for sale as early as the 19th century. It was claimed in 1880 that the firm sold 2.5 million bottles annually.
Some people also associate Moët & Chandon with the fact that it supplied champagne to Queen Elizabeth II and received a royal warrant. In 1971, Moët & Hennessy was founded when the winery combined with Hennessy Cognac. It was an excellent opportunity for both organizations to expand their presence on the global stage.
The history of Louis Vuitton begins with the company’s role as a luggage provider to the French aristocracy. Vuitton invented the flat-topped trunk made of Trianon canvas in 1858 to meet the evolving needs of its consumers and the changing nature of transportation. Vuitton trunks were substantially lighter than the conventional rounded-top ones, effectively sealed, and stacked easily for lengthy journeys.
One of the reasons Louis Vuitton was such a successful brand in the 19th and 20th centuries was the company’s willingness to adapt to the challenges provided by the development of modern transportation. In 1885, it launched its first store in densely populated London. Through the succeeding years, it spread across the entirety of the United States, Asia, and several other countries.
Thus, in a $4 billion merger in 1987, Louis Vuitton, one of the early luxury brands, combined with Mot Hennessy, the top maker of champagne and cognac, established LVMH (Lous-Vuitton-Mot-Hennessy).
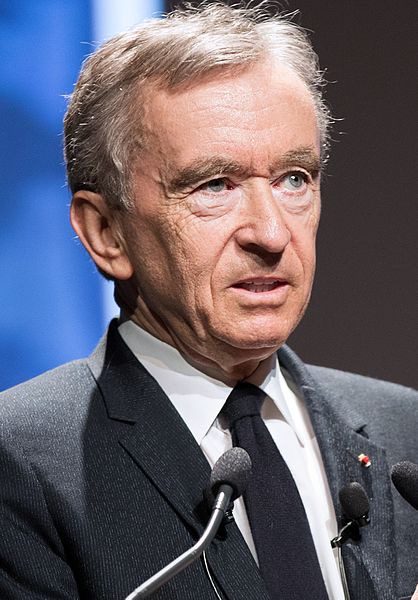
Bernard Arnault: A Key Player in Expanding the Luxury Brand
Since its inception, LVMH has seen one of the fastest and most profitable expansions in business and advertising. This is due in large part to the substantial investments made in the French company by Bernard Arnault, the richest person on Earth as of 2022, with an estimated net worth of $188 billion.
Arnault invested $1.5 billion in a holding company that now controls 24 percent of LVMH in 1988. The same year, he paid another $600 million to increase his stake in LVMH by 13.5 percent. A year later, in 1989, Arnault had spent an additional $500 million and owned 43.5% of the company’s stock. That may be why the executive board voted to make him CEO and board chair.
Nowadays, LVMH oversees more than 60 high-end businesses, the vast majority of which are brand owners in their own right. Givenchy, a French couture and cosmetics house with a 70-year history, was its first such purchase in 1988.
More Acquisitions by the Luxury Giant
LVMH made a series of strategic acquisitions in the 1990s that helped solidify its position in the industry. Also sold to LVMH in 1993 was the Italian manufacturer of fine men’s shoes and other accessories, Berluti. In 1994, it purchased Guerlain, a French cosmetics, skincare, and fragrance business.
Two years later, it added the ready-to-wear fashion house Céline and the luxury leather goods firm Loewe to its portfolio. And in 1997, the company further expanded its offerings by acquiring Sephora, another well-known French cosmetics and skincare retailer. These acquisitions allowed LVMH to diversify its product offerings and solidify its position as a leader in the luxury goods industry.
In the new century, LVMH consolidated a wide range of high-end brands under its wing. These include current and former subsidiaries, spanning a wide range of luxury product categories, from timepieces and jewelry to alcoholic beverages, cosmetics, and even yachts.
Some of LVMH’s subsidiaries include Marc Jacobs, Thomas Pink, Tag Heuer, Gucci Group, Hermes, Emilio Pucci, DKNY, Kenzo, EDUN, Bulgari, Moynat, Repossi, and Jean Patou. Together, these subsidiaries help LVMH maintain a strong presence in various markets, including fashion, accessories, and lifestyle.
LVMH has made several high-profile acquisitions in the cosmetics industry, including Christian Dior and Tiffany & Co. The company also owns several well-known brands, including Fresh, Benefit Cosmetics, Kat Von D Beauty, and Fenty Beauty. These acquisitions have helped LVMH establish a strong presence in the industry and solidify its reputation as a leading luxury goods company.
What Set LVMH Apart from Its Competitors
LVMH distinguishes itself by emphasizing innovation and sustainability. For example, the corporation has established various initiatives to lessen the environmental effect of its operations, such as using renewable energy and developing recycling and trash reduction programs. Furthermore, LVMH has a dedicated team of researchers and designers who are always trying to create new goods and technologies that are more sustainable and ecologically friendly. For example, the Kat Von D Beauty brand features a range of vegan and cruelty-free beauty items. In contrast, LVMH’s Fresh brand has a line of skincare products that use sustainable, all-natural ingredients.
Another distinct feature of LVMH is its extensive distribution network and global reach. The corporation operates retail storefronts, e-commerce platforms, and wholesale distributors in over 70 countries. For example, LVMH’s Fenty Beauty brand, founded by singer and actress Rihanna, has reached a varied worldwide customer base through its online and physical retail presence.
Another distinguishing feature of LVMH is its attention to quality and craftsmanship. The company maintains stringent quality control requirements and invests substantially in research and development to ensure that its products achieve the highest levels of performance and efficacy. This attention to detail and focus on perfection can be found in the company’s extensive product line, which includes everything from high-end skincare and makeup to fragrances and haircare items.
Furthermore, LVMH’s solid financial performance distinguishes the company from its competitors. The company has a long financial stability and growth history and has regularly generated strong financial results. This financial strength gives LVMH the resources and flexibility to invest in innovative technology and products and pursues smart acquisitions and collaborations.
LVMH’s focus on innovation and sustainability, robust distribution network and global reach, commitment to quality and workmanship, and excellent financial performance distinguish the company from its beauty brand competitors.
LVMH’s Luxurious Portfolio: A Wide Range of Quality Products
LVMH is one of the world’s largest luxury goods companies, with a diverse brand portfolio that includes fashion, leather goods, perfume, cosmetics, wine and spirits, jewelry, and watches.
- Fashion: LVMH owns several luxury fashion brands, including Louis Vuitton, Christian Dior, Fendi, Givenchy, and Celine. These companies sell clothing, shoes, and accessories for men, women, and children.
- Leather Goods: LVMH’s portfolio includes many luxury leather goods brands, including Louis Vuitton, Fendi, and Celine, which offer a wide range of high-quality leather handbags, luggage, and accessories.
- Perfume: LVMH’s portfolio includes a number of perfume and fragrance brands, including Christian Dior, Guerlain, and Kenzo. These companies sell perfumes, colognes, and scented candles for both men and women.
- Cosmetics: LVMH’s portfolio includes several luxury cosmetics brands, including Christian Dior, Kat Von D Beauty, Fenty Beauty, Fresh, and Benefit Cosmetics. These companies sell a variety of makeup, skincare, and hair care products.
View this post on Instagram
- Wine and Spirits: LVMH’s portfolio includes many wine and spirits brands, including Mot & Chandon, Hennessy, and Chateau d’Yquem, among others. These companies sell a wide variety of wines, champagne, and spirits, such as whiskey, cognac, and vodka.
- Jewelry: LVMH’s portfolio includes several luxury jewelry brands such as Bulgari, Fred, and De Beers. These companies sell a wide variety of fine jewelry, such as rings, necklaces, earrings, and watches.
- Watches: LVMH’s portfolio includes many luxury watch brands, such as TAG Heuer, Hublot, and Zenith. These companies sell a variety of high-end watches for both men and women.
View this post on Instagram
The LVMH brand stands for the epitome of luxury and opulence. Everything from clothing to timepieces is available at this business. The diversity of its customer base and the variety of the markets it sells are two of the company’s most distinguishing features. The brand is at the forefront of today’s fashion industry thanks to its cutting-edge R&D and a global staff of over 150,000 experts. Globally, LVMH is a prestigious luxury label that has set standards for the entire industry.